There are two key research methods will be used in IRC ,and they are (1) Basic or Fundamental (or horizon scanning or Blue-Sky) Research and (2) Applied or Action (or Proof of Concept or Strategic) Research
Basic or Fundamental Research is the first stage of the Applied or Action Research and both types of research methodology would be used in the IRC to explore, understand, form and describe the problem in some cases solutions According to https://www.formpl.us/blog/basic-research, fundamental research is a type of research approach that is aimed at gaining a better understanding of a subject, phenomenon, or basic law of nature. This type of research is primarily focused on the advancement of knowledge rather than solving a specific problem, but it would be useful in improving understanding and supporting solutions to a problem. It is a major means of generating new ideas, principles, and theories. Typically, basic research can be divided into exploratory (interpretative grounded theory approach) research and descriptive (explanatory) research.
Applied research is a type of research methodology that would be used in the IRC to explore and describe a bottom-up view and to provide answers to specific questions or seek to solve a defined problem or provide innovative solutions to issues and risks affecting an individual, group, or society. This includes identifying a problem, developing a research hypothesis and goes ahead to test these hypotheses via an experiment or field studies, mostly employing empirical methods. It is typically a follow-up research design that further investigates the findings of pure or basic research to validate these findings and apply them to create innovative solutions. It is a bottom-up approach to influence policy/technology via scientific understanding of system behaviour, with the top-down understanding of how others force behavioural change through fundamental science, technology, and policy. Advantages of Applied Research include its validity. It is unbiased because it evaluates empirical evidence to arrive at valid research outcomes. It employs carefully mapped-out procedures, and this makes it a more valid research approach. Qualitative and quantitative data collection methods are used in applied research to gather empirical evidence that is further subjected to experimentation to arrive at valid research outcomes. The focus group interviews, questionnaire surveys, observation, audits, and reviews are popular forms of data collection methods in applied research. It is useful and helps individuals and organizations to find solutions to specific problems. There are three types of applied research.
Applied research and basic or fundamental research are two common methods of inquiry, based on purpose or utility. However, there are key differences between these research approaches, and these will be clearly outlined below:
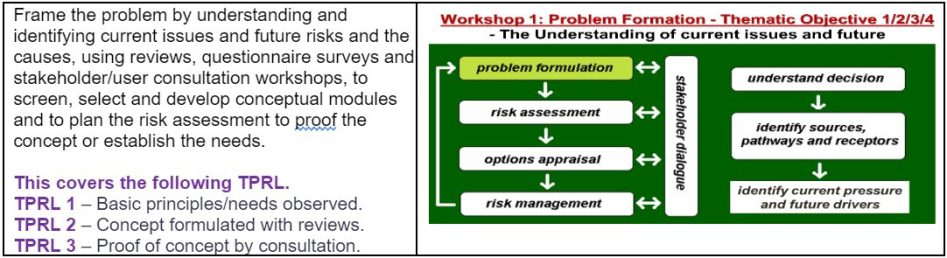
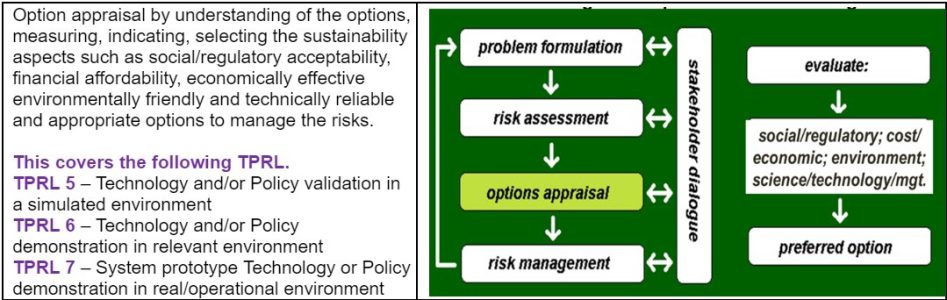
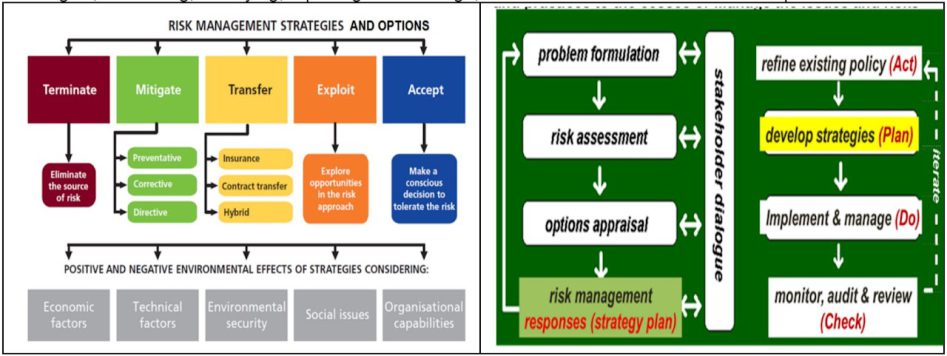
The aim, objective and methodology of a research project are determined by the nature of the problem and intended options. Combination top-down reviews, and bottom-up studies done in Problem Formation stage (stage 1) with the help of stakeholders’ consultation and involvement, would help to determine the ‘Technology and/or Policy Readiness Level (up to TPRL 3), to establish basic principles/needs and formulate concept and prove the validity of concept. Similarly, the other stages would help to achieve the relevant ‘Technology/Policy Readiness Level.